[Updated post :-9 Nov 2015 ]
[ What is Nano? ]
New installation of Windows Server 2016.
Prior version has:
- Windows Server full installation
- Minimal Shell (Min Shell)
- Server Core
It is similar like Server Core but with even smaller footprint. No local UI and no local console. With so minimal footprint, you can increase a number of virtual machine without concern about the overhead required by the operating system. Besides than that, it has less patch and less reboot.
Ideal scenaro:
- Compute host for Hyper-V Virtual machines
- Storage host for Scale out file server
- Container or virtual machine guest OS for cloud native app
[ Scenario]
- Using Windows Server 2016 TP3
[ Set up ]
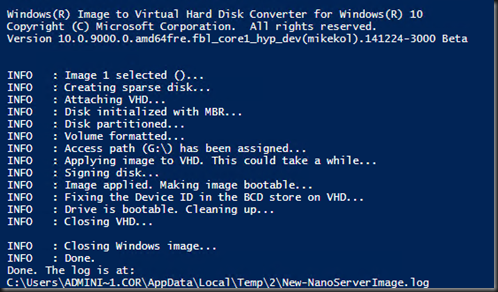
At this moment, installation of Nano is extracting from the windows server 2016 ISO and create an image file using the Convert-WindowsImage.ps1 You will find a folder called “NanoServer”.
- Copy all to your computer
- Execute New-NanoServerImage.ps1 using Windows Powershell
| .\New-NanoServerImage.ps1 |
Create a VHD name “NanoSvr1”. It will create a virtual disk using Convert-WindowsImage
| New-NanoServerImage -MediaPath f:\ -BasePath .\Base -TargetPath .\NanoSvr1 -ComputerName NanoSvr1 –GuestDrivers |
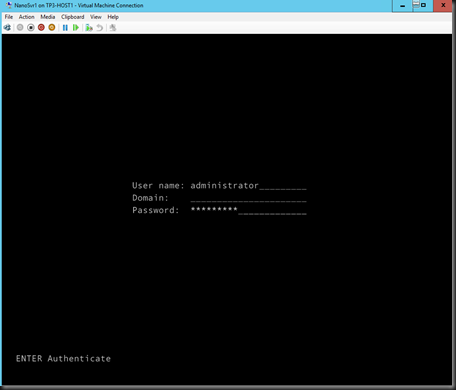
Once a virtual disk has created, you can use Hyper-V Manager to create a virtual machine and attach the virtual disk that you’ve created on previous step.
Enter administrator password that you key in during creation.
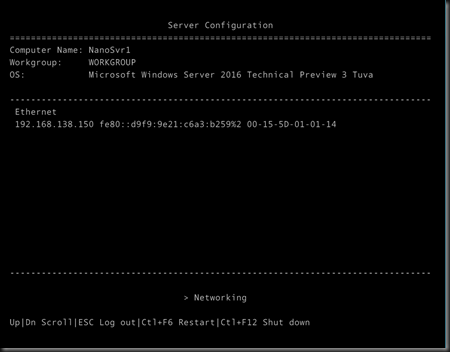
Now we got a Hyper-V host running on Nano installation mode. ![]()
To check how small the footprint, use Inspect Disk on Hyper-V Console
[ Add more packages]
Nano Server ships with several packages that enable more functionality.
- create a folder called dism and copy
- api*downlevel*.dll
- *dism*
- *provider*
from Windows Server 2016 to dism folder.
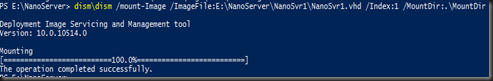
cd NanoServer
md mountdir
| dism\dism /mount-Image /ImageFile:E:\NanoServer\NanoSvr1\NanoSvr1.vhd /Index:1 /MountDir:.\MountDir |
- Add Hyper-V Roles using Add Package
| dism\dism /Mount-Image /ImageFile:.\NanoServer.vhd /Index:1 /MountDir:.\mountdir dism\dism /Add-Package /PackagePath:.\packages\Microsoft-NanoServer-Compute-Package.cab /Image:.\mountdir |
- Dismount drive and commit
dism\dism /Unmount-Image /MountDir:.\MountDir /Commit
[ Management ]
By default, Nano Server will get an ip from DHCP server. You can configure static ip by following below step.
Create a file. Name it as SetupComplete.cmd and enter below code
| powershell.exe -command "Import-Module C:\windows\system32\windowspowershell\v1.0\Modules\Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility\ Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility.psd1; Import-Module C: \windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Modules\NetAdapter\NetAdapter.psd1; $ifa = (Get-NetAdapter -Name Ethernet).ifalias; netsh interface ip set address $ifa static 192.168.138.150" |
Mount the vhd again and execute below command
| md .\mountdir\Windows\Setup\Scripts dism\dism /Unmount-Image /MountDir:.\MountDir /Commit |
At this moment of writing, you only can manage remotely.
Join to domain
| djoin.exe /provision /domain corp.lab.local /machine nanosvr1 /savefile .\odjblob
|
A file odjblob was created. Transfer to Nano Server C:\Temp.
Use Powershell remoting
| Enter-PSSession “192.168.138.150” –Credential “Nanosvr1\administrator” |
Modify some settings using netsh
netsh interface ip set dnsservers name="Ethernet" static 192.168.138.120 primary
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off
Let join to domain and then reboot the server.
| djoin /requestodj /loadfile c:\Temp\odjblob /windowspath c:\windows /localos shutdown /r /t 0 |

Well, at this moment we cannot run Hyper-V roles on a virtual machine. So you may want to transfer this virtual machine to physical server and configure boot from vhd.
|
[Conclusion]
That’s all on our short guide to setup Nano Server for Hyper-V.
We follow the guide from Getting Started with Nano Server :- https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt126167.aspx